Procurement is a critical business enabler in the public sector. According to Statistics, the overall Public Procurement accounts for 13% to 20% of GDP in most countries. This accounts to approximate global spending of around $9.5 trillion per year on the procurement of products and services by public sector firms.

A significant amount of the government’s budget is spent on procuring products and services that affect a wide range of industries such as Engineering, Procurement & Construction (EPC), and), education, and development of other public facilities.
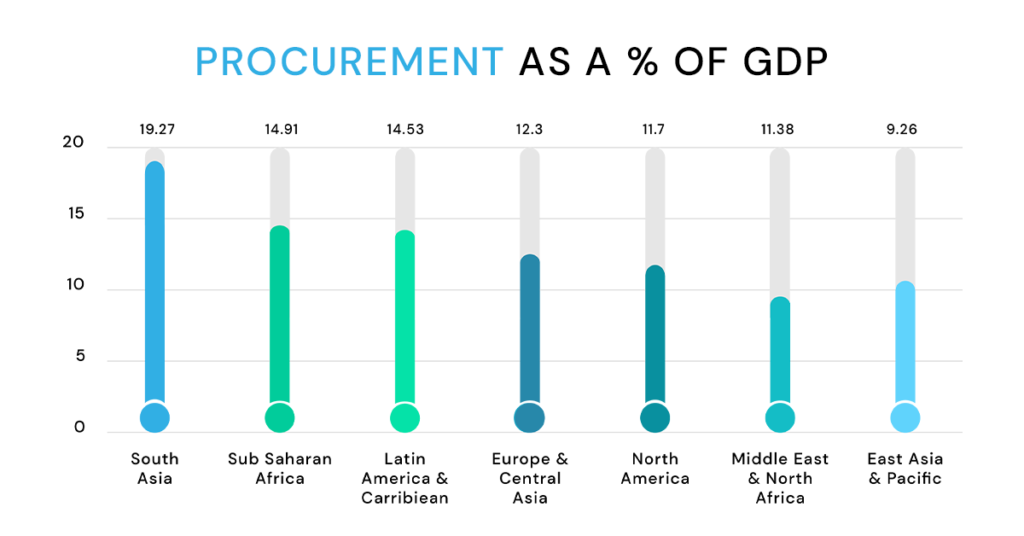
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the difference between Public and Private Procurement processes?
Both private and Public Sector procurement organizations seek to purchase goods and services. The major distinction between the two types of organizations is the goal behind the procurement process. The government-controlled public sector prioritizes societal benefit, whereas the private sector which is headed by individuals and private businesses is mostly aimed at achieving profits. Moreover, the public procurement process usually comes with a lot of regulations, approval hierarchies, budget constraints, etc and is usually slow due to delays at different stages and lack of a proper system to handle the processes.

Public Procurement Process
The public procurement process generally consists of 11 steps:
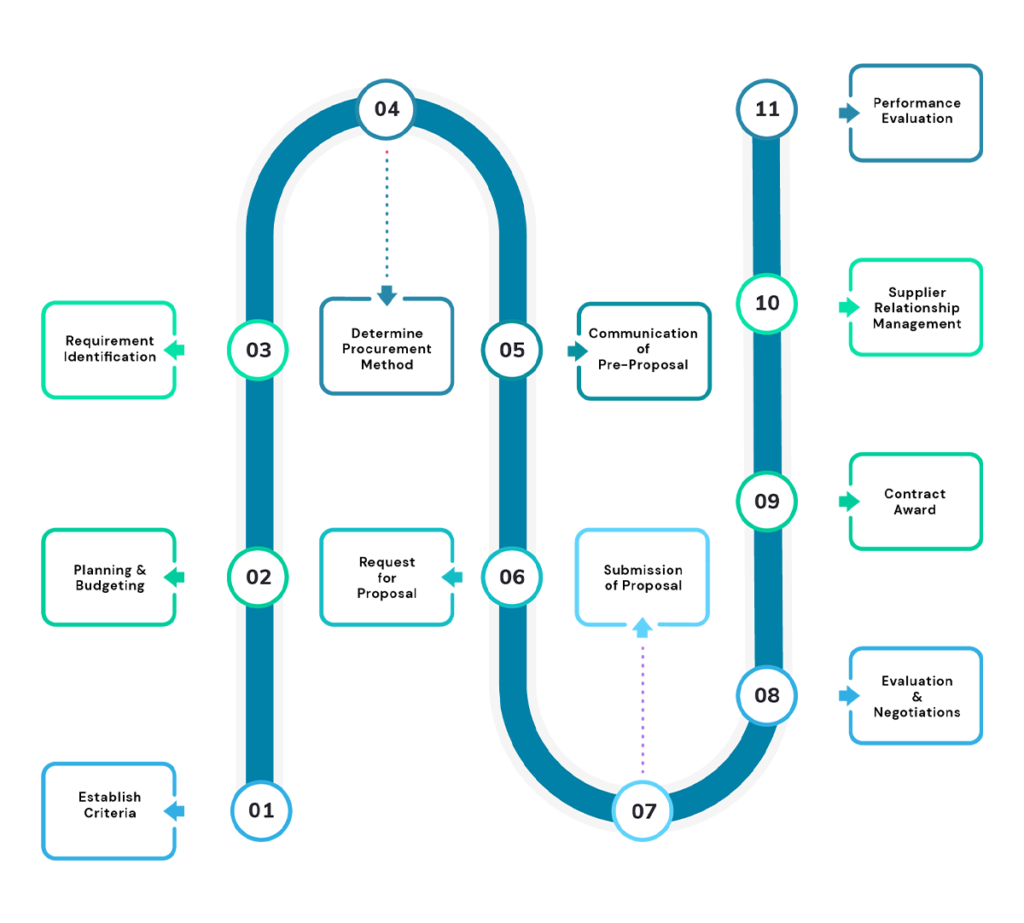
To gather essential products and services, the government or the public sector organizations advertise, gather information, and accept invitations to conduct bid, RFQs, and RFPs, request for letters of interest and negotiations. The replies are then reviewed, evaluated, and awarded depending on the needs of the company, with price not being the only sole determining factor.
Challenges with Procurement in Public Sector
Public sector procurement departments accounts for high amounts of spend in various activities such as tendering and contracting in order to build large infrastructural projects, or purchasing routine office supplies, etc. Recent data on public procurement demonstrates that governments all over the world frequently rely on the private sector to manufacture and manage goods and services. However, the public procurement marketplace includes several loopholes and discrepancies that make the procurement process for a public sector inefficient, time-consuming, and expensive. Furthermore, the introduction of online digital platforms and the proliferation and adoption of e-commerce business models in the private sector are forcing government enterprises to redesign their administrative organizational paradigms.
The following are some of the biggest challenges faced by the public procurement process today:
Spend Management & Control:
The governance structure of Public Sector enterprises is complicated with a strict budget and several parallel governing bodies; such that one department may focus on finding minimum-cost suppliers while another may prioritize acquiring the greatest quality goods or services. Such disagreements can lead to contradictory and ineffective policy enforcement and wastage of government budget and resources.
Introducing New and Sustainable Purchasing Strategies:
Adopting new purchasing techniques and tools can be difficult because organizations are accustomed to procuring goods in their old traditional ways.
Increasing Procurement Visibility:
Achieving transparency and visibility are persistent goals of public sector enterprises. However, since data is dispersed among various organizational units and procurement departments, it is either not completely shared or disclosed leading to redundancies, inaccuracies, or errors.
Supplier-related Problems:
One of the most prevalent procurement issues is finding and vetting vendors. It can be quite a challenging task to keep supply chains running smoothly with so many government regulations and compliances to follow.
Realizing the full value of Analytics:
Understanding the actual potential of procurement analytics to prevent disruption, anticipate revenue, and identify possibilities for savings with advanced modeling and statistical techniques are often challenging in the public procurement processes.
Importance of Strategic Sourcing in Public Procurement
Strategic Sourcing includes activities to minimize supplier base, establish effective vendor communication, and develop long-term supplier relationships to maximize value. Several public sector enterprises utilize Strategic Procurement Software to achieve budget accountability, spending efficiency, and sustainable purchasing with access to a reliable supply of commodities and services that are essential to their operations. Implementation of effective Strategic Sourcing techniques in public sector organizations can result in a greater understanding of how government expenditure is structured and enable optimization of budgeting processes as well as enhanced decision-making.
Strategic Sourcing Best Practices in Public Sector
Adopting strategic sourcing in the public sector may seem to be a difficult endeavor. However, with the implementation of effective strategic sourcing practices and tools, even the most complex public sector procurement challenges can be simplified. Following are the six pillars of strategic sourcing that can significantly impact your public procurement process:
Procurement Strategy
The procurement strategy for public enterprises is designed in line with the organization’s vision, purpose, values, and goals. Such strategies have to be established proactively with collaboration of all units of government entities regarding supplier selection to further meet the requirements of the community and important stakeholders.
Strategic Spend Management
Public sector companies must adopt strategic approaches in spend management in procurement activities to sustain in the competitive environment. Strategic spend management entails long-term planning, establishing company regulations, and utilizing a robust strategic sourcing software platform to predict, categorize, and analyze all business spend data in real time for identifying cost-cutting and savings opportunities. MeRLIN is an automated Strategic Sourcing Solutions that allows organizations to automate upstream activities including category management, spend analysis, supplier relationship management and contracting effectively leveraging access to real-time data, advanced analytics and collaboration capabilities.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Supplier Relationship Management has gained a lot of traction in the public sector due to its tangible and intangible benefits. It helps in effective management of the entire supply base and assists in nurturing a viable pool of possible suppliers that might be beneficial for a company’s procurement strategy. Effective supplier relationship management helps in nurturing supplier relationships through transparent communications, monitoring supplier performance, initiating supplier development programs, etc and building long-lasting strategic partnerships.
Contract Management
Procurement departments need to track procurement Contract Performance over time to guarantee that a public entity’s demands are satisfied, and contract objectives are met. Digitization of contract management processes with a contract repository of digital contracts makes milestone tracking, renewals, etc easily manageable.
Risk Management
Risk mitigation in government organizations necessitates close collaboration between the procurement process, legal activities and resources, and project managers. It begins with the planning stages of a project or procurement process by identifying possible risk areas related to sourcing, contracting, upgrades to new technologies, etc. Digitization of sourcing and procurement processes ensures that procurement processes are streamlined to ensure compliance and risk concerns are taken into account in supplier selections, solicitations, etc.
Adopting e-Procurement
Public procurement processes often require greater transparency and standardized policies to assure authenticity across the organization. Digitization through e-Procurement can enhance the public procurement cycle without disrupting government laws and regulations that are important for the successful governance of public entities. A study by the World Bank revealed that countries that already had an e-procurement system had to make fewer modifications to respond to the new circumstances created by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The adoption of an e-procurement system dramatically decreases requisition-to-order processing expenses, minimizes transaction cycle time, and provides visibility throughout the procurement process. It also makes it easier for suppliers to do business with government bodies by offering interactive online bidding and tracking capabilities.
Following the procurement digital transformation, the next evolutionary step is Procurement 4.0. It is driven by increased digitization, and the use of the latest technologies such as big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and RPA (Robotic process automation) that can transform the entire public procurement function.
Conclusion

Managing procurement in public sector is critical and quite difficult undertaking, because of the rules and standards that are always in place to gain public confidence. By leveraging the best Strategic Sourcing software, companies can improve their procurement strategy and negotiation abilities, and cut down expenses to a minimum to achieve long-term savings and competitive success.
A well-established Strategic Sourcing System can assist public sector organizations in modernizing their procurement processes while considering their unique challenges related to complex governance criteria, transparency, diversified sourcing, and regulatory compliance issues. In case you have any queries regarding strategic sourcing in the public sector, feel free to Contact Us.







One comment
Wonderful post!!! Genuinely loved it! The insights on strategic sourcing in public procurement were great, especially the comparison between public and private processes. I’d love to see more on e-Procurement implementation, real-world success stories, or the role of AI and big data in procurement.